 “We humans have many vestigial features proving that we evolved,” argues Jerry A. Coyne, Ph.D. (pictured left), biology professor at the University of Chicago. Coyne is the author of the book Why Evolution is True. Vestiges are biological features thought to be evolution relics. Scientific evidence, however, is critical; are evolution vestiges fact, or fiction?
“We humans have many vestigial features proving that we evolved,” argues Jerry A. Coyne, Ph.D. (pictured left), biology professor at the University of Chicago. Coyne is the author of the book Why Evolution is True. Vestiges are biological features thought to be evolution relics. Scientific evidence, however, is critical; are evolution vestiges fact, or fiction?
Aristotle (384–322 BC) originated the vestiges theory. Even though WIKIPEDIA considers the theory as “controversial and not without dispute,” the carte blanche use of vestiges continues as supporting evidence for the popular “evolution is true” argument.
Recent advances in biotechnology, however, are challenging the scientific validity of the evolution vestiges theory.
Origin of Vestige Theory
Observing the reduced size of eyes in the underground mole-rat, the 4th century BC Greek philosopher, Aristotle, wrote in his book, the History of Animals that their eyes were “stunted in development.” Centuries later, Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, a French naturalist, in 1798 was the first to link the concept of “vestiges” with evolution. Geoffroy (pictured right) explained –
“Because Nature never works by rapid jumps… She always leaves vestiges of an organ, even though it is completely superfluous.”
Geoffroy collaborated with Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829), a French colleague who listed many vestigial structures in his book Philosophie Zoologique. Commenting on Aristotle’s mole-rat observations, Lamarck explained that since it had received less sunlight –
“the mole has altogether lost the use of sight: so that it shows nothing more than vestiges of this [eye] organ.”
As Darwin explained in his Autobiography, “the subject [evolution] was in the air.” Capitalizing on the fray was Robert Chambers (pictured right). As an entrepreneur and publisher, Chambers anonymously released his Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation in 1844. Chambers championed and popularized Geoffroy’s and Lamarck’s link between vestiges and evolution. Chamber’s book soared into a sensational best-seller. Even Queen Victoria reportedly read and became fascinated with the book. The sales of Chamber’s book far exceeded that of Darwin’s The Origin of Species through the 1880s. Chamber’s book emerged as a philosophical tipping point in society. Vestiges, however, had yet to be scientifically validated.
Chamber’s book soared into a sensational best-seller. Even Queen Victoria reportedly read and became fascinated with the book. The sales of Chamber’s book far exceeded that of Darwin’s The Origin of Species through the 1880s. Chamber’s book emerged as a philosophical tipping point in society. Vestiges, however, had yet to be scientifically validated.
Human Vestiges
 German anatomist Robert Wiedersheim (pictured left) further extended the work of Geoffroy, Lamarck, and Chambers with his book entitled The Structure of Man (1893). According to Wiedersheim –
German anatomist Robert Wiedersheim (pictured left) further extended the work of Geoffroy, Lamarck, and Chambers with his book entitled The Structure of Man (1893). According to Wiedersheim –
“Organs having become wholly or in part functionless… For the greater part, Organs, which may be rightly termed Vestigial.”
The concept of vestiges eventually emerged as the stepping stone to gaining public belief in evolution. In North America, as in Europe, the broadening influence of evolution paralleled the rise of the Progressive Movement into the 20th century. The purpose of this secular movement was to create a utopian society. However, given public resistance to evolution, the strategy turned to science education. Evolution was thought to be scientific.
Public Education
The progressive movement influenced publishers to incorporate evolution into their biology textbooks; Darwin legitimized racism. At the same time, lobbyists in state and federal legislatures worked to expand nationwide mandatory public education programs. In 1914 American writer George William Hunter incorporated evolution into his new biology textbook entitled Civic Biology (cover page pictured right). As WIKIPEDIA explains –
“The views espoused in the book about evolution, race, and eugenics were common to American Progressives.”
Civic Biology, like many other texts of the time, paraded vestiges as a fact. The New Standard Encyclopedia (1931), published by Funk & Wagnalls Company, described evolution as “facts from zoology, botany, and geology.” According to Funk & Wagnalls –
“[Concerning] the place of man in the evolutionary plan… The vestigial structures show [a] connection with mammals who walked on four feet.”
Evolution, race, and eugenics were broadly taught as scientific facts. Eugenics, meaning “the production of good offspring,” was adopted by the progressives to engineer their new utopian society, a plan eventually implemented by Nazi Germany. Hunter explains in the section entitled The Races of Man –
“At the present time, there exist upon the earth five races or varieties of man… the highest type of all, the caucasians, represented by the civilized white inhabitants of Europe and America.”
In essence, the non-civilized were relegated as vestiges – the relics of evolution. More racist excerpts from other sections of the book are in Appendix I. These sections include the Evolution of Man, Eugenics, Parasitism and its Cost to Society, and The Remedy.
Butler Act
To challenge the progressive movement, state laws were enacted. In Tennessee, the legislature passed the Butler Act in 1925. The statute read –
“That it shall be unlawful for any teacher… to teach instead that man has descended from a lower order of animals.”
John T Scopes (pictured right), a 24-year-old science and math teacher in Dayton, Tennessee, was accused of violating the act. In defiance of the act, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) offered to defend anyone accused of teaching the theory of evolution.
Scopes Trial
 Tennessee’s prosecuting team, led by district attorney Tom Stewart, included Herbert and Sue Hicks, Ben B. McKenzie, and William Jennings Bryan. As a dominant force of the Democratic Party and former member of the US House of Representatives, Bryan passionately opposed evolution on religious and humanitarian grounds.
Tennessee’s prosecuting team, led by district attorney Tom Stewart, included Herbert and Sue Hicks, Ben B. McKenzie, and William Jennings Bryan. As a dominant force of the Democratic Party and former member of the US House of Representatives, Bryan passionately opposed evolution on religious and humanitarian grounds.
In Scopes defense, the team included Clarence Darrow (Darrow pictured left; Bryan pictured right), an ACLU attorney, Arthur Garfield Hays, Dudley Field Malone, W.O. Thompson, F.B. McElwee, and Charles Francis Potter. The trial became internationally known as the Scopes Trial, also known as the Monkey Trial. Vestiges played a critical role during the court proceedings. Horatio Newman, a zoologist at the University of Chicago, was called as an expert witness. Newman testified that –
“There are, according to Wiedersheim, no less than 180 vestigial structures in the human body, sufficient to make of a man a veritable walking museum of antiquities.”
Media Frenzy
The eight-day trial captured international attention, igniting a media frenzy, with more than 200 newspaper reporters from all parts of the country and even from London. Trained chimpanzees performed on the courthouse lawn while Chicago’s WGN radio station provided on-the-scene live coverage. For many, the trial was a mocking spectacle.
Charged for teaching evolution on May 5, the trial started on July 10 and found Scopes guilty on July 21, 1925. However, in January 1927, the Tennessee Supreme Court overturned Scopes conviction based on a procedural technicality. Registered as a Socialist, he later ran for the Kentucky congress in 1932. Defeated, Scopes later became financially successful by drilling for oil in Texas and Louisiana.
Hollywood Capitalizes
Hollywood eventually capitalized on the frenzy. In support of the progressive movement, their productions shrewdly crafted their audience to question the biblical account of creation.  In 1955, American playwriters, Jerome Lawrence and Robert E. Lee, debuted their fictional account of the trial. The play’s title, Inherit the Wind, was cleverly quoted from Proverbs 11:29 –
In 1955, American playwriters, Jerome Lawrence and Robert E. Lee, debuted their fictional account of the trial. The play’s title, Inherit the Wind, was cleverly quoted from Proverbs 11:29 –
“He that troubleth his own house shall inherit the wind.”
In 1960, Lawrence and Lee released their play as a Hollywood film. The film, by the same title, was then revised and released three more times; in 1965, 1988, and 1999. Each film received numerous entertainment awards. The progressive movement has since continued to sell their belief in evolution successfully. Far from the Butler Act era, the teaching of evolution as a scientific fact is now a government requirement in most public education systems – globally. Aristotle’s vestige theory has long played as an essential selling point. According to the state-sponsored University of California website, Evolution 101, vestiges are –
“an adaptation from the organism’s ancestor, but that evolved to be nonfunctional.”
California presents vestiges as carte blanche proof of evolution but without any validating scientific evidence. Now, with the availability of new 21st century technologies, testing the “evolution vestiges fact, or fiction” question can yield a valid scientific answer.
Human Appendix
In Why Evolution is True, Coyne argues that “We humans have many vestigial features proving that we evolved.” In the words of Coyne, again, “the most famous is the appendix.” Continuing the argument –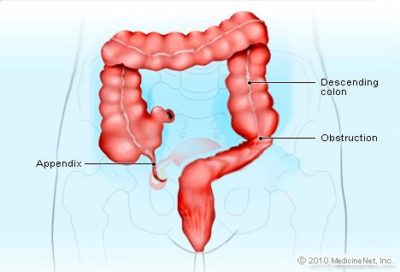
“Our appendix is simply the remnant of an organ that was critically important to our leaf-eating ancestors but is of no real value to us [humans].”
Writing for the Richard Dawkins Foundation, in an article entitled “Five things Humans No Longer Need,” science writer Laura Spinney concurs with Coyne –
“Vestigial organs are parts of the body that once had a function but are now more-or-less useless. Probably the most famous example is the appendix.”
Medical experience seems to support Coyne’s and Spinney’s arguments. Since the first appendectomy in 1735 on an 11-year-old boy, removing the appendix has become a common procedure. Appendectomies now account for 2.1% of all operating-room procedures in the United States.
Immunity
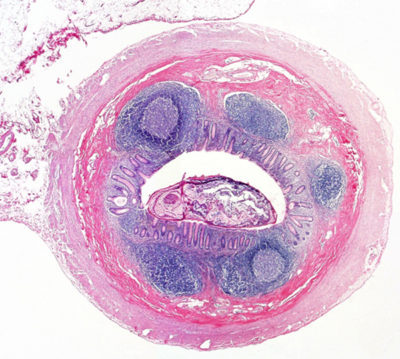 While removing the appendix can be performed safely, the human appendix plays an essential role in immunity. Advances in biotechnologies over the past century have revolutionized our understanding of immunology. In the human embryo, lymphoid tissues start developing in the appendix. The lymphoid tissues produce lymphocytes (pictured in appendix left), a type of white blood cells (WBCs) that are responsible for producing antibodies.
While removing the appendix can be performed safely, the human appendix plays an essential role in immunity. Advances in biotechnologies over the past century have revolutionized our understanding of immunology. In the human embryo, lymphoid tissues start developing in the appendix. The lymphoid tissues produce lymphocytes (pictured in appendix left), a type of white blood cells (WBCs) that are responsible for producing antibodies.
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large protein used by the immune system to neutralize and remove antigens from the body. Antigens include pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and prions that are capable of causing serious disease and death.
Good Bacteria
The appendix serves as a haven for good bacteria. Jennifer Warner, a science writer for WebMD, in the article “Appendix May Actually Have a Purpose,” notes –
“The lowly appendix may have a purpose after all. New research suggests that the seemingly useless organ [the appendix] provides a safe haven for good bacteria to hang out in the gut.”
Gabrielle Belz, laboratory head in the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute Division of Molecular Immunology, explained to ScienceDaily –
“Popular belief tells us the appendix is a liability… However, we may wish to rethink whether the appendix is so irrelevant for our health… A balanced microbiome is essential for recovery from bacterial threats to gut health, such as food poisoning.”
William Parker, M.D., Ph.D. (pictured right), professor of experimental surgery along with R. Randal Bollinger, M.D., Ph.D., of Duke University, studied the role of the appendix in the immune system. In speaking to ScienceDaily,  Parker explained –
Parker explained –
“Our studies have indicated that the immune system protects and nourishes the colonies of microbes living in the biofilm. By protecting these good microbes, the harmful microbes have no place to locate. We have also shown that biofilms are most pronounced in the appendix.”
The appendix plays an essential role in balancing bacteria, the good with the bad. ScienceDaily published Parker’s comments in the article “Appendix Isn’t Useless At All: It’s A Safe House For Good Bacteria.” Rather than “useless,” the appendix is a haven for the gut’s biofilm. Also known as a microbiome, these three-dimensional structures are metaphorically known as the “cities for microbes” – critical players in sustaining good microbes in the gut. Parker’s research team, including Heather F Smith, Sanet H. Kotzéd, and Michel Laurine in their more recent research paper entitled “Morphological Evolution of the Mammalian Cecum and Cecal Appendix” (2017), published by ScienceDirect, said –
“This is the first time they have been statistically validated. The association between appendix presence and lymphoid tissue provides support for the immune hypothesis of the appendix.”
Embryonic Appendix
 During the second trimester of the human embryo, lymphocytes start aggregating in the appendix. Loren G. Martin, professor of physiology at Oklahoma State University, in the article What is the Function of the Human Appendix,” explains –
During the second trimester of the human embryo, lymphocytes start aggregating in the appendix. Loren G. Martin, professor of physiology at Oklahoma State University, in the article What is the Function of the Human Appendix,” explains –
“Lymphoid tissue begins to accumulate in the [embryonic] appendix… and reaches a peak between the second and third decades of life, decreasing rapidly thereafter and practically disappearing after the age of 60.”
Concurring with Martin, Rebecca Fisher of the Center for Functional Anatomy & Evolution of the John Hopkins School of Medicine, gives a similar explanation –
“The [lymphocyte] follicles increase steadily in number to a maximum of two hundred at about fifteen to twenty years of age and decline back to about one hundred by thirty years of age and decline further, even to the disappearance, throughout the rest of life.”
ScienceDaily article entitled “Immune Cells Make Appendix ‘Silent Hero’ of Digestive Health” said it this way –
“New research shows a network of immune cells helps the appendix to play a pivotal role in maintaining the health of the digestive system, supporting the theory that the appendix isn’t a vestigial — or redundant — organ.”
Worse yet, for Darwin’s theory of natural selection proceeding through “slight, successive changes,” the appendix is not even found in many mammals advanced to be one of our ancestors. Darwin’s dilemma intensifies.
Genesis
Biotechnology has proved vestiges to be only an ancient philosophical construct. Evolution relics do not exist. Aristotle’s vestige theory busted. Coyne’s “proof of evolution” is empty rhetoric. Evolution, it seems, never happened. The Progressive Movement was philosophical, not scientific. Given evolution is a belief system and not a scientific fact, evolution should only be taught accordingly. Tennessee’s much maligned Butler Act was, after all, very wise. Embracing the philosophy of evolution tragically resulted in the bloodiest century in human history. The theory of evolution justifies racism.
Only theories compatible with the Genesis account have eventually been scientifically validated. Carolus Linnaeus (pictured right), the Swedish naturalist who formalized our modern system of naming plants and animals, only sees “perfection,” not vestiges during the Scientific Revolution.
“I saw the infinite, all-knowing, and all-powerful God from behind.… I followed His footsteps over nature’s fields and saw everywhere an eternal wisdom and power, an inscrutable perfection.”
Developing a scientific consensus on the mechanisms of evolution still remains speculative.
Evolution Vestiges Fact, or Fiction is a Theory and Consensus article.
Darwin Then and Now is an educational resource on the intersection of evolution and science, highlighting the ongoing challenges to the theory of evolution.
Move On
Explore how to understand twenty-first-century concepts of evolution further using the following links –
-
- The Understanding Evolution category showcases how varying historical study approaches to evolution have led to varying conclusions. Subcategories include –
- Studying Evolution explains how key evolution terms and concepts have changed since the 1958 publication of The Origin of Species.
- What is Science explains Charles Darwin’s approach to science and how modern science approaches can be applied for different investigative purposes.
- Evolution and Science feature study articles on how scientific evidence influences the current understanding of evolution.
- Theory and Consensus feature articles on the historical timelines of the theory and Natural Selection.
- The Biography of Charles Darwin category showcases relevant aspects of his life.
- The Glossary defines terms used in studying the theory of biological evolution.
- The Understanding Evolution category showcases how varying historical study approaches to evolution have led to varying conclusions. Subcategories include –
Appendix I
Excerpts from Civic Biology, written by George William Hunter (1914)
| Evolution of Man. – Undoubtedly there once lived upon the earth races of men who were much lower in their mental organization than the present inhabitants. |
| The Races of Man. – At the present time there exist upon the earth five races or varieties of man… the highest type of all, the caucasians, represented by the civilized white inhabitants of Europe and America. |
| Eugenics. – When people marry, there are certain things that the individual, as well as the race, should demand. The most important of these is freedom from germ diseases… The science of being well born is called eugenics. |
| Parasitism and its Cost to Society. – Hundreds of families such as those described above exist today, spreading disease, immorality, and crime to all parts of this country… They take from society, but they give nothing in return. They are true parasites. |
| The Remedy. – If such people were lower animals, we would probably kill them off to prevent them from spreading… we do have the remedy of separating the sexes… [for] preventing intermarriage and the possibilities of perpetuating such a low and degenerate race. Remedies of this sort have been tried successfully in Europe. |



