 “Human evolution is the lengthy process of change by which people originated from apelike ancestors,” explains the Smithsonian Institute exhibit (pictured left) entitled “Introduction to Human Evolution.” Continuing their explanation –
“Human evolution is the lengthy process of change by which people originated from apelike ancestors,” explains the Smithsonian Institute exhibit (pictured left) entitled “Introduction to Human Evolution.” Continuing their explanation –
“Scientific evidence shows that the physical and behavioral traits shared by all people originated from apelike ancestors and evolved over a period of approximately six million years.”
The source of the Smithsonian’s description is rooted in history. Although this was also Charles Darwin‘s central argument in The Descent of Man (1871), this explanation had emerged before the sixteenth century, long before Darwin, highlighting a critical issue.
By the Modern Colonial Era, the theory of evolution had begun to weave its way into the fabric of Western academic circles. This idea presented a new intellectual justification for colonialization. At the time Darwin published The Descent of Man, a broadening acceptance of even human evolution was emerging, especially within progressive circles. Within his sphere of contemporaries, Darwin confidently explains –
“Man must be included with other organic beings in any general conclusion respecting his manner of appearance on this earth.”
The one critically important issue, however, that is not addressed by Darwin or even the Smithsonian Institution, centers on the scientific evidence for the theory of evolution.
Ape to Man
In The Origin of Species, Darwin proposed his new theory of evolution, natural selection. For Darwin, evolution involves “the preservation and accumulation of small inherited modifications.” As an outcome of this  process, Darwin predicted finding an “inconceivable” number of transitional links –
process, Darwin predicted finding an “inconceivable” number of transitional links –
“The number of intermediate and transitional links, between all living and extinct species, must have been inconceivably great.”
To validate this theory scientifically, then, the physical existence of an “inconceivably great” number of transitional links is critical. As evidence for proof, Darwin referred to the geological record. However, Darwin provides only the following statement as evidence in Chapter VI of The Descent of Man (pictured right) –
“Nor should it be forgotten that those regions which are the most likely to afford remains connecting man with some extinct ape-like creature have not as yet been searched by geologists.”
Without any observable and measurable evidence, Darwin’s theory, then, is only speculative, not a scientifically valid approach. Darwin, however, never claimed to be a scientist. Without physical evidence of transitional ape links, the arguments presented in The Origin of Species and The Descent of Man are only philosophical.
Smithsonian Human Evolution Exhibit
The displays presented by the Smithsonian human evolution exhibit only infer, as did Darwin, that transitional links exist. Critically important, though, the Smithsonian exhibit does not include even one scientifically valid transitional link. The exhibition uses the following reason –
“Scientists do not all agree, however, about how these species are related [connected] or which ones simply died out. Many early human species — certainly the majority of them – left no living descendants. Scientists also debate over how to identify and classify particular species of early humans, and about what factors influenced the evolution and extinction of each species.”
Scientist’s Critique
The Smithsonian exhibit does not identify a single transitional link for good reasons – none exist. In the words of evolutionary biologist Richard Lewontin at Harvard University –
“No fossil species can be established as our direct [human] ancestor.”
 According to the American Museum of Natural History, paleontologists Niles Eldredge (pictured left) and Ian Tattersall –
According to the American Museum of Natural History, paleontologists Niles Eldredge (pictured left) and Ian Tattersall –
“One could confidently expect that as more hominid fossils were found, the story of human evolution would become clearer. Whereas if anything, the opposite has occurred.”
As Stephen Jay Gould explains in the book Panda’s Thumb –
“Most hominid fossils, even though they serve as a basis for endless speculation and elaborate storytelling, are fragments of jaws and scraps of skulls.”
Harvard physical anthropologist Earnest Hooton noted that attempts of “alleged restorations of ancient types of man have very little, if any, scientific value and are likely only to mislead the public.” And they have.
Jerome Lejeune (pictured right), a geneticist from the University of Paris, France, penned the following protest –
“The neo-Darwinist is now reaching the point of dignity in the history of science that the Ptolemaic [geocentric] system … reached long ago. We know that it does not work. And that is interesting. Because from the actual structure of the chromosome, we can demonstrate that the human species did not come from a progressive humanization of a pre-human.”
Geoffrey Clark from the University of Chicago opines –
“Scientists have been trying to arrive at a consensus about modern human origins for more than a century. Why haven’t they been successful?”
The answer is increasingly apparent. The absence of any supporting physical evidence has eliminated the possibility of scientifically validating the once-popular theory of human evolution.
“Modern apes, for instance, sprang out of nowhere,” according to South African anthropologist Lyall Watson –
“They have no yesterday, no fossil record. And the true origin of modern humans—of upright, naked, toolmaking, big-brained beings—is, if we are, to be honest with ourselves, so equally mysterious matter.”
In the new book entitled Science & Human Origins, Casey Luskin arrives at the now inescapable conclusion –
“Despite the hype promoted by many evolutionary paleoanthropologists, the fragmented hominin fossil record does not document the evolution of humans from apelike ancestors.”
Without evidence of transitional links to a common ancestor in the fossil record, molecular, or genetic paleontology, Darwin’s dilemma intensifies. The Smithsonian Institute has a history of promoting evolution fiascos. Regrettably, the Smithsonian and Darwin apelike comparisons legitimatized racism.
Genesis
The Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History human evolution exhibit has no scientific basis to support the theory of human evolution. Sadly, our country’s Natural History Museum still promotes a philosophy  parading as science. Smithsonian storytelling, not science, is not uncommon.
parading as science. Smithsonian storytelling, not science, is not uncommon.
While evolution scientists remain paralyzed in their attempts to develop a consensus on a cohesive theory of evolution, the available physical evidence continues to be compatible with the Genesis account written by Moses.
Galileo Galilei (pictured right), an Italian astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and mathematician, played a significant role in the scientific revolution during the Renaissance. Galileo has since become recognized as the “father of observational astronomy” and the “father of modern physics. In the words of Galileo during the Scientific Revolution –
“I am inclined to think that the authority of the Holy Scripture is intended to convince men of those truths which are necessary for their salvation, which, being far above man’s understanding, can not be made credible by any learning, or by any means than revelation by the Holy Spirit.”
Evidence for common ancestry and transitional links underscores why the theory of evolution remains speculative but not scientifically valid.
Smithsonian Human Evolution Exhibit is a Fossil Record article.
Darwin Then and Now is an educational resource on the intersection of evolution and science, highlighting the ongoing challenges to the theory of evolution.
Move On
Explore how to understand twenty-first-century concepts of evolution further using the following links –
-
- The Understanding Evolution category showcases how varying historical study approaches to evolution have led to varying conclusions. Subcategories include –
- Studying Evolution explains how key evolution terms and concepts have changed since the 1958 publication of The Origin of Species.
- What is Science explains Charles Darwin’s approach to science and how modern science approaches can be applied for different investigative purposes.
- Evolution and Science feature study articles on how scientific evidence influences the current understanding of evolution.
- Theory and Consensus feature articles on the historical timelines of the theory and Natural Selection.
- The Biography of Charles Darwin category showcases relevant aspects of his life.
- The Glossary defines terms used in studying the theory of biological evolution.
- The Understanding Evolution category showcases how varying historical study approaches to evolution have led to varying conclusions. Subcategories include –
2020 Update
One potential transitional human link is listed, stating –
“All of these traits convinced [Raymond] Dart [in 1925] that the Taung Child was a bipedal human ancestor, a transitional form.”
No human evolution tree of life diagram was published.
Evolution 101 – Human Evolution
This section does not address transitional links
This section does not include a tree of life diagram depicting human evolution.
Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History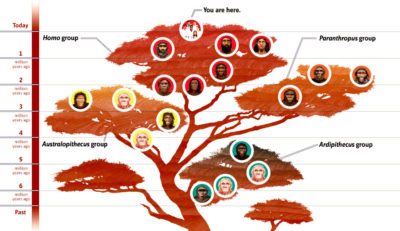
Human Evolution Evidence – this section does not address transitional links
Human Family Tree – this section includes the graphic (pictured right) but without any further information.
Evolution is a philosophy, not a valid scientific theory


